Top Web and Mobile Development Trends to Watch in 2026

The web and mobile development trends in 2026 are reshaping how businesses build digital experiences. From AI-powered apps to progressive web apps (PWAs), developers now have tools to create faster, smarter, and more immersive applications. In this blog, we explore the top trends that are driving the industry forward and how they can improve performance, engagement, and user satisfaction.
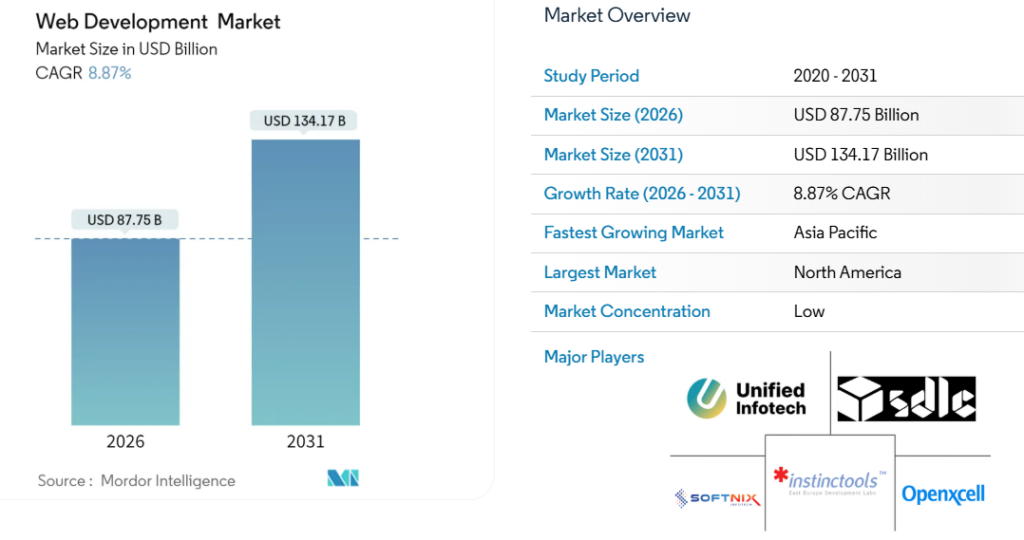
“Mordor Intelligence estimates the web development market at USD 87.75 billion in 2026, growing to USD 134.17 billion by 2031 (8.87% CAGR), driven by e-commerce, mobile-first strategies, and AI integration.”
1. AI-Powered Web and Mobile Development
Artificial Intelligence continues to dominate the development landscape in 2026. AI is no longer just a code-completion tool, it now drives web and mobile development trends in 2026 across UI design, backend automation, and predictive analytics.
“Some reports suggest AI could affect up to 300 million jobs globally by 2030, which means developers must move beyond tasks AI can easily automate.”
Key Applications of AI in Development:
- Auto-generating UI components that align with brand guidelines
- Predicting app performance before launch
- Smart debugging, testing, and accessibility audits
- AI-driven personalization for content and interfaces
- Chatbots and voice assistants for 24/7 engagement
AI empowers developers to focus on creative solutions and user experience, while automation handles repetitive tasks.
2. Mobile-First and Next-Gen Connectivity
Mobile-first design is now a requirement, not an option. With over 60% of users browsing via smartphones and tablets, developers must optimize websites and apps for mobile performance.
“In markets like India, employers are expected to add millions of new jobs in 2026, fueled by mobile-first usage and rapid digitization.”
Best Practices:
- Use responsive layouts with Flexbox and CSS Grid
- Optimize images and assets for faster load times
- Implement vertical and touch-friendly navigation
- Combine with 5G/6G and edge computing for ultra-fast, real-time apps
Next-gen networks enable AR/VR interactions, IoT connectivity, and seamless streaming for richer mobile experiences.
3. Headless CMS for Flexible Content
Headless CMS platforms are revolutionizing content management. They separate content from presentation, allowing developers to create dynamic and personalized experiences across web, mobile, and IoT devices.
Advantages:
- Faster content delivery via API-first architecture
- Freedom to use frameworks like React, Vue, Next.js, or Svelte
- Marketing teams can manage content without developer dependency
- Supports multi-channel publishing (web, apps, kiosks, wearables)
4. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs combine the reach of the web with the functionality of native apps. They are lightweight, fast, and work offline, making them ideal for businesses targeting global or low-connectivity audiences.
Benefits of PWAs:
- Single codebase for web and mobile
- Offline functionality with service workers
- Push notifications for engagement
- Seamless, app-like experiences across devices
5. Immersive Experiences with AR, VR, and Spatial Computing
AR, VR, and spatial computing are expanding beyond gaming into education, retail, healthcare, and training.
What Developers Should Focus On:
- Interactive 3D product visualizations
- Virtual classrooms and corporate training modules
- Gesture-based controls and AI-assisted interactions
- Real-time simulations for retail and industrial applications
6. Cross-Platform and Low-Code Development
Cross-platform frameworks like Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin allow developers to maintain a single codebase for iOS, Android, and web.
Why It Matters:
- Reduces development time and costs
- Ensures consistent UX across devices
- Supports AI-driven adaptive apps
Low-code and no-code tools further democratize development:
- Rapid MVP creation
- Internal tools and dashboards without deep coding knowledge
- Seamless integration with AI features
7. WebAssembly and High-Performance Web Apps
WebAssembly allows developers to run C++, Rust, and C# code in browsers, providing near-native performance for demanding applications.
Use Cases:
- 3D modeling, CAD, and video editing in the browser
- Heavy computation for scientific and financial apps
- High-performance gaming and immersive experiences
8. Motion UI and Enhanced User Engagement
Motion UI is no longer optional. Subtle animations, micro-interactions, and scroll effects make websites engaging and improve storytelling.
Key Elements:
- Hover animations and interactive icons
- Scroll-based transitions
- Micro-interactions for buttons, cards, and menus
- Seamless navigation and transitions
9. Voice Search and Accessibility
Voice search is becoming standard, especially among Gen Z and Gen Alpha. Developers need voice-optimized websites and apps for better accessibility and engagement.
Benefits:
- Hands-free, faster interaction
- Better accessibility for visually impaired users
- Supports AI-powered conversational interfaces
10. Security and Ethical Development
With apps handling sensitive data and AI integrations, security is paramount. Developers should focus on:
- Secure serverless functions
- Static code analysis and vulnerability scanning
- Privacy-first AI implementations
- Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations
“AI can generate large amounts of code, but developers still need to catch security loopholes, fix vulnerabilities, and ensure production readiness.”
Final Thoughts
The web and mobile development trends in 2026 emphasize speed, intelligence, accessibility, and immersive experiences.
“Job outlook: The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects about 7% job growth for web developers and digital designers from 2024–2034.”
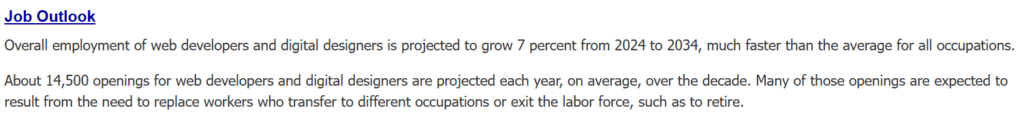
Businesses that adopt AI, PWAs, WebAssembly, low-code tools, and voice interfaces will stay competitive while delivering high-performing and user-friendly apps. Web development is no longer just about coding, it’s about creating meaningful digital experiences that scale across platforms and devices.
Related articles



